How many people can be in a group?
3
Can we work with our friends?
Yes
Where can I create it?
You can create it as a website, Prezi or Google slides
What can I bring in?
Nothing sharp. Anything that you are not sure about, just ask your teacher.
You can bring in coloured paper, cardboard, polystyrene, sticky tape, blue tac
Antarctic Treaty
Watch the following two videos and then answer the questions below:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wsrYGvMr4Nc
http://www.abc.net.au/btn/story/s4107405.htm
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s87KIX6owk0
1. Who owns Antarctica?
2. What is the Antarctic Treaty?
3. Why does the Antarctic Treaty exist?
Extension: Research about Mawson using YouTube
Week 3
Use 3 Workstations to research the following
- Who owns Antarctica? What is the Antarctic Treaty? (cite source)
- Information about Antarctica (e.g. weather, plants, animals, who works there) (cite source)
- Write a short report about one animal in Antarctica (a little under than half a page with information such as diet, where it lives, how long it lives for, interesting facts about it, how they have babies, who are their prey and predators and anything else you can find out about it). (cite source)
- How is Global Warming affecting Antarctica? (cite source)
Workstation 1: Ipads
You are to watch the following videos
Workstation 2: Chromebooks
You are to explore the following sites
Workstation 3: Books and KidCyber
Explore books provided to answer the questions
Go to http://www.kidcyber.com.au and search for Antarctica
Explore books provided to answer the questions
Go to http://www.kidcyber.com.au and search for Antarctica
Map Instructions
- Student get a laptop and get into pairs and then they log onto Gmail.
- Open your maps on Drive
- Go to the 3 little bars and click on it
- Go to Your Places → Maps
- Go to “Create a New Map”
- Explain that the Ss will be scientists and that they will be visiting the top 4 areas most affected by climate change. Get them to go to the following website http://www.scientificamerican.com/slideshow/top-10-places-already-affected-by-climate-change/ which shows the top 10 locations most affected by climate change.
- Click on “Untitled Layer” and give it a title as “Global Warming Affected Areas”.
- Place a marker on Uganda and show how to add pictures and videos.
- Run a line from Sydney to Uganda and show students the distance.
- Place a marker in Switzerland in the Alps and include pictures and videos.
- Run a line from Uganda to Switzerland.
- Show how to save the map by clicking on “Preview” mode and then show how the finished work would be.
- Also show students how they can measure area of locations using the “Draw a line” feature so they can learn about area and perimetre and be able to compare countries and continents.
- Allow students to create the next three destinations and encourage them to share it with the teacher. They should aim to include pictures, capture the main idea of what the affected problem is and videos relating to the area. They are to work in pairs or in threes.
TERM 3
Week 1 Global Warming
Students in book write down “What are the top three major threats to our planet?”
Write down in your book definition of Global Warming
Watch the following video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RHrFBOUl6-8
6G Compete against students from 6W in terms of points on Linoit.
6G: STF6GREEN Password: student
6W: STF6WHITE Password: student
THINK: Is Global warming or Climate Change even real?
Can we believe everything remember Fake Octopus website which was shown in Term 2 http://zapatopi.net/treeoctopus/
Students must get into groups or they can work individually based on their class groups. They learn about how they can research climate change/global warming on Google. “Global Warming for Kids”
http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/climateChange/whatis.html
Answer the following questions below on butcher’s paper.
- What is climate change/global warming?
- Do you think Global warming is being caused by humans? Why or why not?
- What can humans do to have sustainable futures?
- Why do we need to be concerned about climate change?
- How will climate change affect you and your family?
- What could you do to help prevent climate change?
- What do you think will happen if we don’t try to stop climate change?
- What should others do to prevent climate change?
- Who will be the most affected by climate change?
- What are some interesting facts I have found out about Global Warming?
TERM 2
Week 1
Features of a good map.
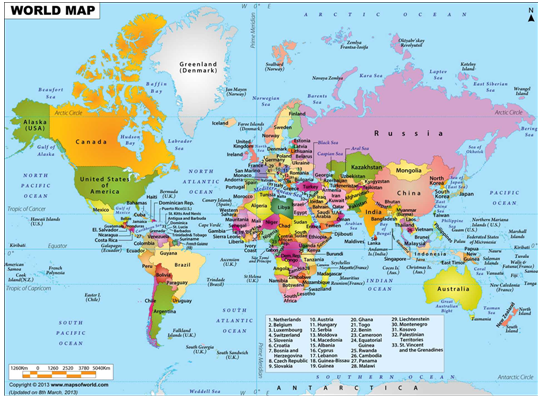
A good map should tell you what it is about (title), which direction north is (orientation), when the map was made or updated (date), who made the map (author), what the symbols mean (legend or key), how distances on the map relate to distances on the ground (scale), where to find selected places on the map (index), how to find places on the map (grid), and where the map's information comes from (sources)
https://www.google.com.au/maps/@46.8215054,-6.6911108,8943000m/data=!3m1!1e3
Explore places you know or have visited
What country were you born?
Where were your parents/grandparents born?
Has anyone visited another country?
What other places (countries) do we know of?
What separates the countries?
Can we name the oceans?
http://mapmaker.nationalgeographic.org/
Play this game
http://world-geography-games.com/
Balloon World Map
1. Color and cut out the continents.
2. Color and cut out the continent and ocean labels.
3. Glue the continent labels onto the pictures of the continents.
4. Blow up your blue balloon.
5. Glue the North Pole where you tie your balloon.
6. Draw the Prime Meridian and Equator to divide your balloon into hemispheres.
7. Glue the labeled continents where they should be located on your balloon globe.
8. Glue the ocean labels onto your balloon globe.
9. Glue the compass rose onto your globe. Be careful that the directions are pointed the correct way.
Extension Tasks
Students can explore world map and discover facts and statistic about countries they are unfamiliar with. http://mrnussbaum.com/interactive-world-map/
Students can explore other geography games on
http://world-geography-games.com
Week 2
Learn to Read World Map
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=swKBi6hHHMA
Using blank world map students record,
- Hemispheres
- Poles
- Lines of latitude (equator, tropic of cancer, tropic of capricorn, arctic circle, antarctic circle)
- Zones (Tropic, Temperate, Polar)
- Line of Longitude (Prime Meridian, meridian)
Make sure you understand the following terms.
Practise your reading map skills
Explore latitude
http://earthguide.ucsd.edu/earthguide/diagrams/latitude/index.html
Explore longitude
http://earthguide.ucsd.edu/earthguide/diagrams/longitude/index.html
Find the place
http://earthguide.ucsd.edu/earthguide/diagrams/latitude_longitude/index.html
Latitude
The angular distance of a place north or south of the earth's equator.
Parallels
Imaginary lines that run east and west on a map. Parallels represent degrees of latitude, or how far a place is away from the equator. The equator's latitude is 0° and the poles are 90° south and north. One degree of latitude equals about 69 miles.
The Antarctic Circle
The Antarctic Circle lies three-quarters of the way between the equator and the South Pole.
The Arctic Circle
Three-quarters of the way between the equator and the North Pole lies the Arctic Circle. Above this line is the Arctic region, where nights last for 24 hours in the middle of winter. It is known as the Land of the Midnight Sun because in summer the sun never sets.
The Equator
This imaginary circle goes around the middle of the earth for 24,902 miles. It divides the Northern Hemisphere from the Southern Hemisphere and is exactly half way between the North and South Poles.
The Tropic of Cancer
A parallel line of latitude that is a quarter of the way from the equator to the North Pole. During the summer solstice, the sun is directly overhead.
The Tropic of Capricorn
This line of latitude is a quarter of the way from the equator to the South Pole. During the winter solstice, the sun is directly overhead.
Longitude
The angular distance of a place east or west of the Greenwich meridian
The International Date Line
An imaginary line where the date changes one day when passed. It is one day earlier east of the line than it is on the west.
Meridians
Imaginary lines that run north and south on a map from pole to pole. Meridians express degrees of longitude, or how far a place is away from the prime meridian. The prime meridian runs through Greenwich, England.
Grid
Longitude is used together with latitude to form a grid on which it is possible to locate any place on the earth.
Practise your reading map skills
Explore latitude
http://earthguide.ucsd.edu/earthguide/diagrams/latitude/index.html
Explore longitude
http://earthguide.ucsd.edu/earthguide/diagrams/longitude/index.html
Find the place
http://earthguide.ucsd.edu/earthguide/diagrams/latitude_longitude/index.html
Record coordinate and name of place in your geography book.
Week 4 (Extra)
- Look at the text Mirror- Jeanie Baker https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fBCBcAqQI_E
- Locate Australia and Morocco on world map.
- Record location on worksheet. Remeber use directional language
- Watch the Lonely Planet video of Morocco https://www.lonelyplanet.com/morocco
- Using Venn diagram record similarities and difference between Australia and Morocco.
Morocco
Natural Resources
What are natural resources?
Natural resources are useful raw materials that we get from the Earth. They occur naturally, which means that humans cannot make natural resources. Instead, we use and modify natural resources in ways that are beneficial to us. The materials used in human-made objects are natural resources.
Watch the following video
https://www.turtlediary.com/video/natural-resources-of-the-earth.html
Complete the following quiz
https://www.turtlediary.com/quiz/natural-resources-of-the-earth.html
Extension:
https://www.turtlediary.com/quiz/natural-resources.html
How people have damaged the environment?
(Username: STFyear6rocks Password: student
Student can use google maps and the following links
Week 5 Task Cards
- Deforestation
- Pollution
- Endangered wildlife
- Climate change/Ozone layer
- Drought
Student can use google maps and the following links
- Deforestation: Honduras, Nigeria, The Phillippines
- Pollution: China (Linfen), Ukraine (Chernoby), Iran (Ahvaz)
- Endangered Wildlife: Ivory-Billed Woodpecker (North America), Amur Leopard (East Russia), Javan Rhinoseros (Indonesia)
- Climate change: Austria (The Alps), The Arctic (The Northwest Passage), Kiribati (Island Nations)
- Drought: Ethiopia, Somalia, Sudan
http://www.unicef.org/drought/drought-countries.htmWeek 5 Task Cards
Week 5
- Students will investigate Australia to improve students general knowledge.
- In groups students will research
- Location
- States & Territories (Capital Cities)
- Climate
- Landmark
- Population
- Flora
- Fauna
- Students will do this by
1. Completing Australia Jigsaw to create an Australian Map
2. Label each state and territory
3. Locate each capital city and mark it on map of Australia.
4. Shade the map according to climate zones.
5.Locate 3 features found in each state/ territory
6. Name flora emblem of each state/territory
7. Write a short paragraph about 4 native Australian animals.
8. Complete Thinking Trek
Week 6
Environmental Issues in Australia
- Students are to investigate 1 environment in Australia that has been impacted on by humans.
- Students can choose
- Shoalhaven Urbanisation https://www.shoalhaven.nsw.gov.au/soe/default.htm
- Great Barrier Reef http://www.wwf.org.au/what-we-do/oceans/great-barrier-reef#gs.JWMDDWo
- Kakadu National Park http://www.environment.gov.au/topics/national-parks/kakadu-national-park
- Timbarra Gold Mine Tenterfield
- Kosciusko National Park
- Students are to (information recorded in all student books)
- Describe its location
- Describe its features
- Explain diversity of flora, fauna, vegetation coverage, natural resources, population and land use.
- How have humans adapted and/or modified the environment?
- Investigate human impact on the environment and create a cause and effect chart.
6. Who manages the environment?
7. How is the environment managed?








No comments:
Post a Comment